Corona Vaccine: Can the result of the Covid-19 Test come out wrong?
Scientists say that the most important way to test the corona virus in the human body is so sensitive that dead viruses or fragments of earlier infections can also be found in it.
Scientists believe that a person is infected with the corona virus for about a week, but even after that, his corona test can be positive for several weeks.
Researchers say that the reason for this may also be that the figures on the scale of the corona epidemic are higher than the estimates.
Although some experts say that how to find a reliable way to investigate corona in which every case of infection can be registered, it has not yet been decided.
Professor Karl Henegan, a researcher involved in this research, says that the new way of testing should be at a cut-off point rather than when the virus is found or not found, to indicate that a small amount of the virus Due to this, the result of the test can be negative.
They believe that finding fragments or fragments of the old virus in the corona virus test helps explain why cases of infection are steadily increasing while the number of people arriving in hospitals is steadily decreasing.
Oxford University's Center of Evidence-based Medicine reviewed evidence from 25 studies in this regard, placing samples of positive tests in a petri dish to see if the virus numbers were growing there.
This method is called scientific 'viral culture' which can tell whether the test that has been done has found an active virus that is able to increase its number or found dead virus or fragments that cannot be grown in the laboratory. can.
BBC Health correspondent Nick Triggle's analysis
Scientists have been aware of this difficulty associated with the virus test since the beginning of the epidemic and this once again shows why the data of the Kovid-19 are not correct.
But what does it matter? Statistics were less available at the beginning of the epidemic but as time went by, more figures were found. Confusion has increased due to the large amount of information about testing and R numbers.
But it is true that in the whole of the UK, the incidence of corona infection is less than in many European countries. As far as the spread of infection is concerned, it can be said broadly that we have been successful in preventing it. And this is when the lockdown has started to be relaxed a bit with the arrival of summer.
But it cannot be denied that the biggest question now is what will happen next, winter days are coming and children are also starting to study in schools.
Health workers in Britain are assuming that the country is currently in strong condition and it seems that more cases of infection can be avoided in the coming months.
But the government and people are also taking all precautions regarding this because it is believed that another round of epidemic could start if not taken seriously.
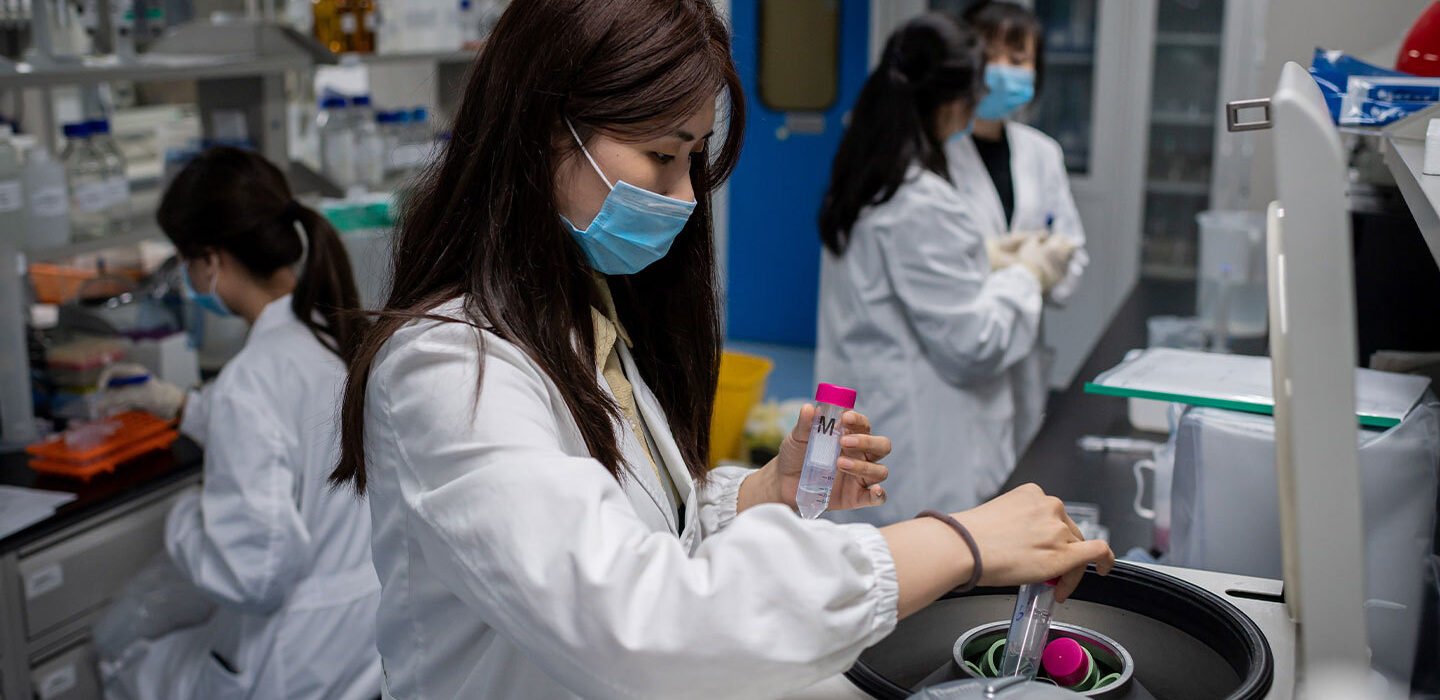
How is Covid-19 tested?
An effective method of corona virus testing is said to be the PCR swab test in which chemical attempts are made to identify the genetic material of the virus and then study it.
The test specimen has to go through several cycles at the laboratory before sufficient virus can be found.
The number of times the virus has been recovered tells us how much virus is there in the body, whether there are parts of the virus or the whole virus.
It also points towards how infectious the virus is in the body. It is believed that if the test tried more often to get the virus, then there is less scope for the virus to grow in the laboratory.
Risk of incorrect test result
But when you are tested for corona virus, you often get a yes or no answer. What is the amount of virus in the sample and whether the case is active infection or not. It is not known from the test.
A person who has a large amount of active virus in the body and whose body has found only fragments of dead virus in the sample - the results of both tests will be positive.
Professor Henegan is among those who have gathered information about how the death toll from Corona is being recorded. Based on this, Public Health England has improved its way of keeping data.
According to him, according to the facts found so far, the effect of corona virus infection "starts to decrease automatically after a week".
He says that it will not be possible to see if the active virus was found in every sample tested. In this case, if scientists can identify a cut-off mark for the amount of virus in the test, then cases of wrong positive results can be reduced.
This will reduce the rate of positive cases of chronic infections and reduce the overall infection count.
Professor Henegan says that this will help many people who are quarantining themselves on the basis of testing and can help understand the current true state of the corona epidemic.
Public Health England believes that the true result of the Corona virus test can be found through virus culture.
The organization says that they are also conducting an analysis in this direction recently and are working with laboratories to avoid the risk of erroneous positive results. He is also trying to determine how the cut-off point can be set for testing.
Although the organization also says that many different testing kits are in use for the corona test, the results of using these kits are understood in different ways and therefore it is difficult to reach a certain cut-off point. .
But Professor Ben Newman of the University of Reading says that cultivating a patient's specimen is no small task.
He says, "With such a review, the culture of the SARS-COV-2 virus can be wrongly linked to the possibility of spreading its infection."
"It is not certain" how long the virus can remain contagious after recovering from corona, says epidemiologist Professor Francesco Venturelli, who works in the Emilia-Romagna region of Italy, badly affected by the Corona virus, in March .
They say that according to some studies done on viral culture, viruses have been found in the body of about 10% people even eight days after recovering from infection.
He says that the peak of the Corona epidemic came before Britain in Italy and that "for several weeks, we had been assessing cases of corona infection more than the reality." This is because people who had been infected earlier had positive results even after recovering. ''
But as the peak decreases, this situation also improves.
Professor Openshaw of Imperial College, London, says PCR tests are a "highly sensitive way of identifying the genetic material of viruses that have survived in the body".
"These tests are not evidence of corona virus infectivity," he says. But doctors believe that it is extremely unlikely that the virus is infectious in the body even after ten days of infection."